Definition and Working Principle of Centerless Grinding Machine
Basic Knowledge: Definition and Working Principle of Centerless Grinding Machines
In modern manufacturing, the development of precision machining technologies directly affects product quality and production efficiency. As a highly efficient external cylindrical grinding solution, the centerless grinding machine plays a vital role in metal processing.
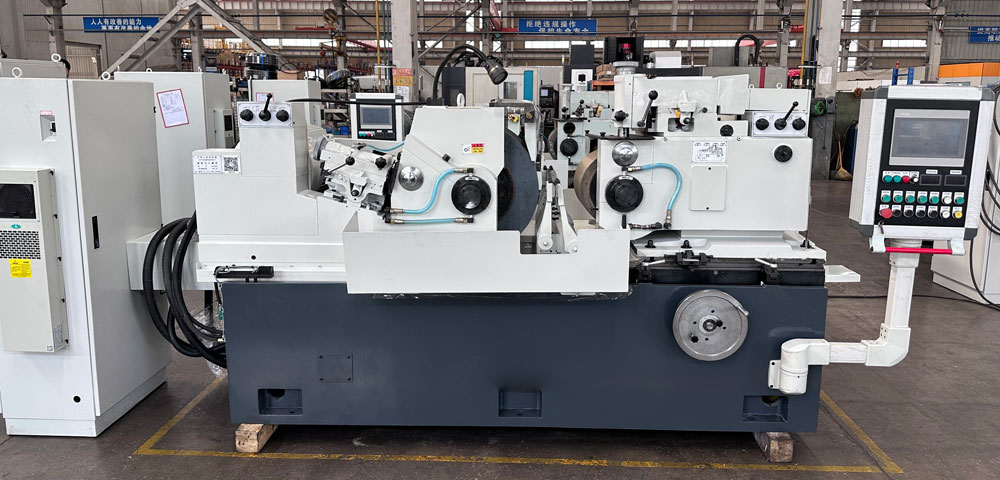

1. What Is a Centerless Grinding Machine?
A centerless grinding machine performs grinding without the need for centers or chucks to hold the workpiece. Unlike conventional cylindrical grinders, it uses a grinding wheel, a regulating wheel, and a support blade to continuously grind parts, making it ideal for long shafts and bar stock.
2. Main Types of centerless grinding machines
Through-feed type: For continuous grinding of bar stock in mass production.
In-feed type: Suitable for stepped or complex-shaped parts, like bearing rings.
CNC centerless grinding machine: Offers high precision and automation for precision parts.
High-speed type: Designed for industries like aerospace and automotive to boost efficiency.
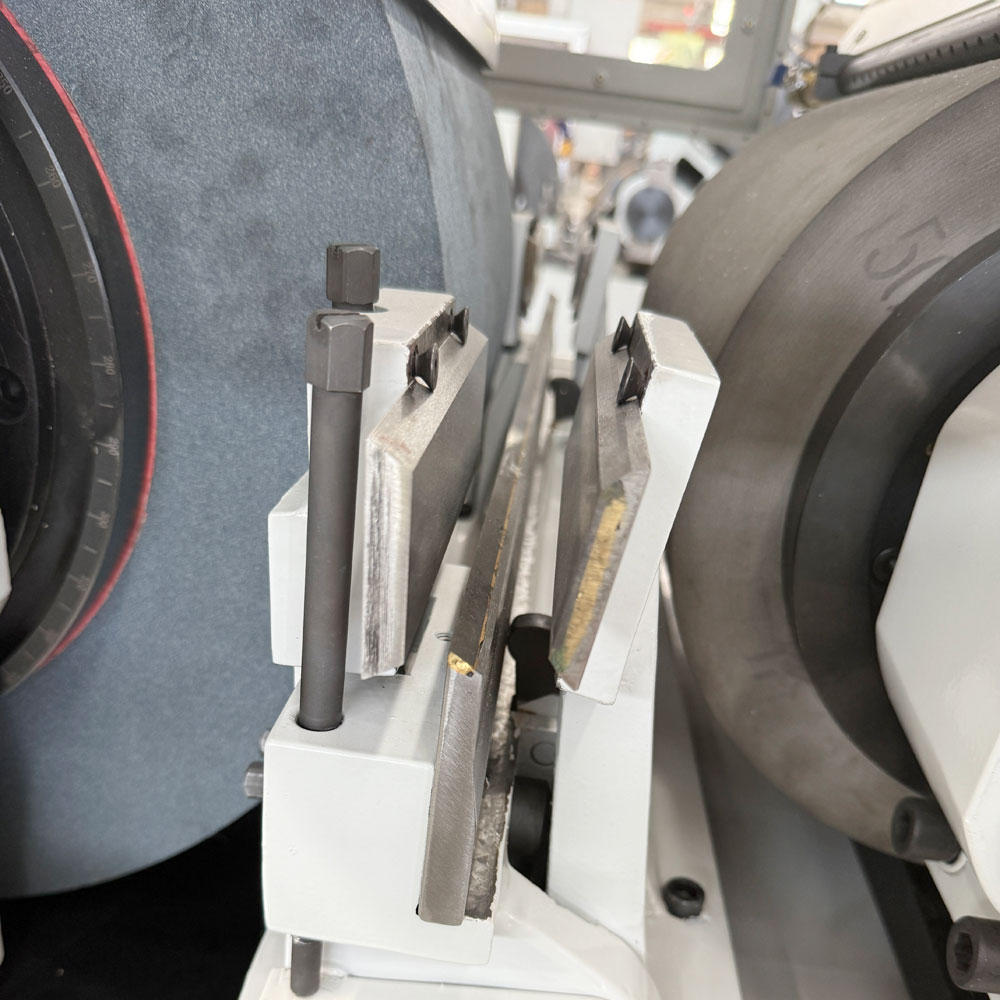
3. Working Principle and Process Flow
The workpiece is placed between a fast-rotating grinding wheel and a slower regulating wheel. A support blade underneath holds the part in position.
Process Steps:
Feeding: Bar is loaded into the machine.
Guiding: Workpiece enters between the wheels.
Grinding: Material is removed by the grinding wheel.
Discharging: Finished part exits the machine.
(Optional) Inspection: Online measurement ensures consistency.

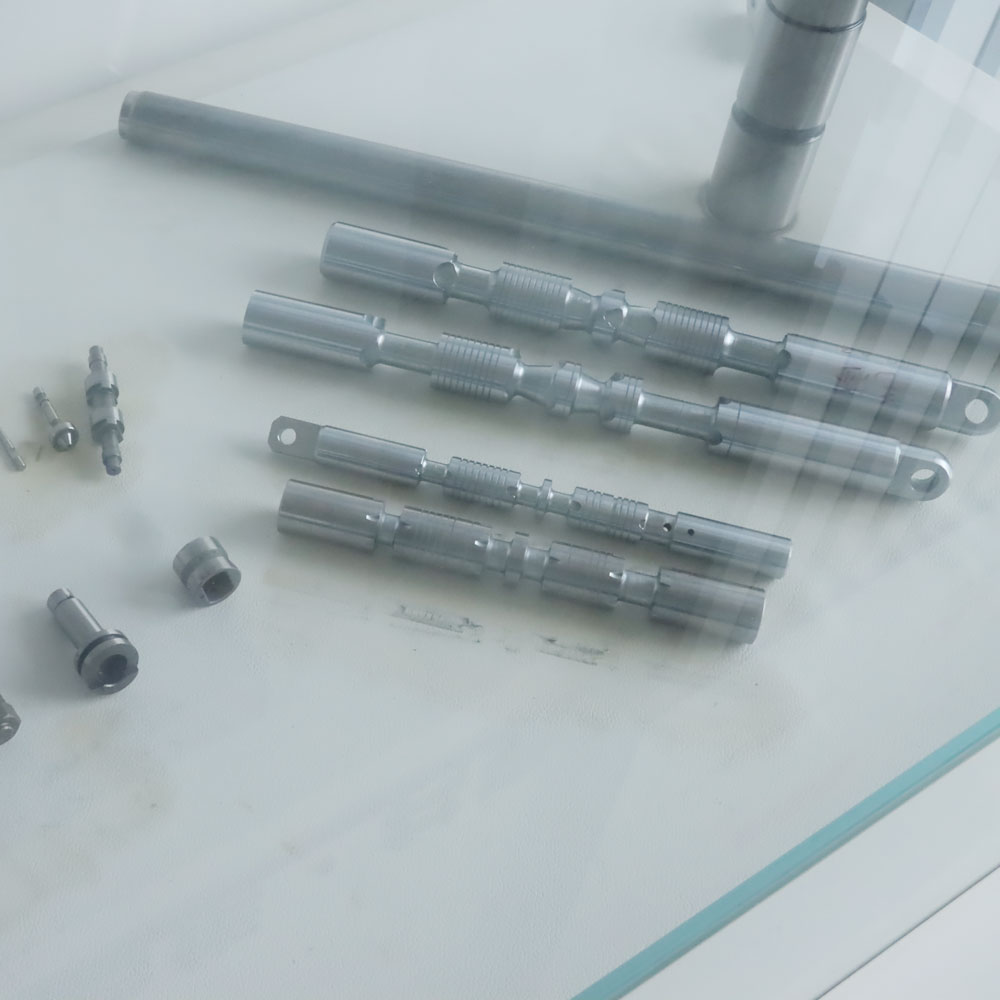
4. Industrial Applications
Automotive: Piston pins, camshafts, crankshafts, and drive shafts.
Aerospace: High-precision shafts for landing gear and engines.
Bearings: Rollers, inner/outer rings requiring tight tolerances.
Medical: Surgical tool shafts, implant connectors.
Tooling: Drill shanks, taps, and milling tool bodies.
5. Key Advantages
No clamping required: Saves time and boosts efficiency.
Continuous operation: Ideal for automated production lines.
High precision: Tolerance up to ±0.002 mm, surface finish Ra 0.1 μm.
Ease of operation: Especially with CNC control.
Material versatility: Handles steel, stainless steel, ceramics, etc.
Low maintenance: Simple structure, low failure rate.
6. Application in Bar Stock Grinding
Ideal for:
Mass production: standard shafts and spring steel bars.
Precision machining: instrument and guide shafts.
Hard materials: hardened steel and carbide.
Automated lines: Easily integrated with robots and loaders.

7. Development Trends
Smart manufacturing: IoT and sensors for remote monitoring.
Higher accuracy: Advanced abrasives and servo control.
Eco-friendly design: Efficient cooling and energy-saving systems.
Flexible production: Supports small-batch, multi-type manufacturing.
8. Conclusion
Centerless grinding machines, with their unique design and high efficiency, are indispensable in today’s manufacturing. From automotive to aerospace and medical industries, they ensure quality and productivity. As technology evolves, centerless grinding machines will continue to grow smarter and more efficient, driving industrial progress and competitiveness.